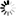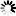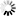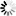5.5kW High Vacuum Fume Extractor Filter For Laser Cutting
1. The fume comes from the processing will be sucked into the extractor through the hood, first the fume passes the 1st layer spark intercept steel mesh which will ranmify the fume to avoid residual sparks enter into HEPA filter layer directly.
2. Finally, the fume enters the second layer of HEPA filter cartridge for ultimate purification.
3. Its filtration efficiency can reach 99.9%.
4. As the filtering precision of the main filter cartridge reaches the indoor emission standards, the filtered clean air can be directly discharged indoor through the air vent in the back of the extractor.
5. According to the extractor's work intensity and the amount of dusts, the usage life of the filter cartridge is different.
1.The high vacuum fume cleaner has a front connector, and can be connected to various professional suction connector, suction welding gun or breathing masks through a hose of Φ44mm,by connecting with hose of Φ44mm and professional nozzle,it also can be used in robot and welding machine's fume purification.The nozzle is fixed on the welding gun and moves with the welding gun to absorb welding smoke simultaneously, also be used in the welding test and in the cleaning of the training sites.
2.The purifier can connect a variety of magnetic suction nozzle through the hose, or connect 2-3 pieces of high vacuum suction welding guns.
3. Mobile high vacuum fume & dust purifier is light with powerful suction. The purifier is rational in design,which allows it to be moved freely. It contains three high vacuum turbine fan units.
4. On the control panel, there are Fan switch, Power switch, Power indicating light and automatic cleaning
Model | KSG-3.4A | KSG-5.5A |
Treatment of air flow | 450±10 m3/h | 700±10 m3/h |
Motor Power | 3.4 kW | 5.5 kW |
Voltage | 3×380 V/50 Hz | 3×380 V/50 Hz |
Filtering area | 20 m2 | 20 m2 |
Cleaning Methods | Automatic Cleaning | Automatic Cleaning |
Compressed Air | 0.5-0.6 MPa | 0.5-0.6 MPa |
Filtration efficiency | >99.9% | >99.9% |
| Filtering Precision | ≥0.3um | ≥0.3um |
| Filter Cartridge | 2PCS | 2PCS |
| Dusting Interface | 2pcs(φ44 mm) | 3 pcs(φ44 mm) |
Noise | ≤72±5dB(A) | ≤72±5dB(A) |
| Demission | 700×700×1850 mm | 700×700×1850mm |
Weight | 265±10Kg | 295±10Kg |

Shanghai Kaisen Environmental Technology Co.,Ltd has beenalways committed to designing, R&D and manufacturing of industrial dust collectors.Since 2007 we had been engaged in dust collectors for ten years.Our products are extensively applied to the processing of welding, cutting, grinding, painting, casting, chemical, wood processing, paper and other industries.


WHAT ARE WELDING FUMES, AND WHY ARE THEY HAZARDOUS?
Welding Fume Extractor Systems You've now doubt heard during training that welding fumes are unhealthy, but may not realize just how dangerous they are. Basically, welding fumes are a toxic combo of gases and particles that are released into the air during the welding process. Approximately 5% of these fumes come from the metal being welded, the other 95% come from the consumables used during the welding process.
The particles in welding fumes are classified under two size ranges, referred to as "fractions." Inhalable fractions are particles up to 100 µm (microns), which equates to 0.1 mm in size, and can be inhaled through the mouth and nose. Alveolar (respirable) fractions are much smaller (up to 10 µm) and most welding fume particles are smaller than 0.1 µm, which puts them in the "ultra-fine" category. The smaller the welding particles released into the air, the more harmful they are to the lungs. This is because they can infiltrate deeper into the lungs.
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN YOU INHALE WELDING FUMES?
The small particulates in welding fumes are inhaled through the nose and mouth. From there, they reach the esophagus or windpipe. From the windpipe, it's a short trip to the bronchial tubes and lungs. Because these particles are so small, they can actually penetrate cell walls, where they then cause mutagenic changes in the body. Translation: welding fumes are a known cause of lung cancer.
Inhalable oxide particles in welding fumes:
Aluminum oxide
Iron oxide
Magnesium oxide
Lead oxide
Fluoride
Copper oxide
Manganese oxide
Chromium (III) compounds
Nickel and cobalt oxides
GASES ARE A PROBLEM, TOO
It's not just particles that pose a health risk, it's the argon gas in shielding gas, gases from paint, oil or solvents on the work-piece (including hydrogen chloride and cyanide), and carbon monoxide created by the welding process. Besides damaging the respiratory tract and being a trigger for cancer, there's also the risk of suffocation.