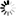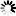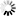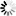Model NO.
UN4
Current
AC Current
Model
Un4
Application
Rod, Blade, Strip Butt Welder
Transport Package
Plywood Box
Specification
CCC, ISO, CE
Trademark
KIA-IND
Origin
USA and China
HS Code
8515219000
Production Capacity
100sets Per Year
Welding Range:
63mm
Cooling Way:
Water Cooling
Control:
Manual
Frequency Range:
Low Frequency
Electric Current:
AC
Type:
Butt Welder
1. UN4 type butt welder is a manual eccentric clamping mechanism. The base and the lower electrode are fixed on the welding seat plate. When the handle is rotated, the eccentric wheel presses the welding element through the upper plate of the clamp, and the distance between the upper and lower electrodes can be adjusted by the eccentric sleeve. When the eccentric is released, the spring makes The electrode pressure is removed.
2. UN-25-50-100-150 type butt welding machine first selects the jaw according to the shape of the weldment. If the weldment is a bar, the jaw can be directly configured with the welder; if the weldment is shaped, it should be customized according to the shape of the weldment. Jaw.
3. Adjust the jaws; align the two center lines of the jaws, and place the two test bars in the lower jaw positioning groove to see if the two bars are aligned. If it can be aligned, the welder can be used; if it is not right, the jaws should be adjusted. Loosen the fastening screw first when adjusting.
12 Re-adjust the adjusting screw 14 and appropriately move the lower jaw to obtain the best position, and then tighten the fastening wire 12.
4. Adjust the distance of the jaws according to the requirements of the welding process. When the joystick is at the leftmost end, the gap between the jaw electrodes should be equal to the difference between the extension length of the weldment and the amount of extrusion; when the rightmost end of the joystick is used, the electrode spacing is equivalent to the extension length of the two weldments, plus 2-3 Millimeter (ie the original position before welding), this distance adjustment is obtained by the adjusting screw (1). The splicing ruler helps you adjust the parameters.
5. Test welding; in order to prevent the instantaneous overheating of the weldment before the test welding, the number of adjustment stages should be increased step by step. In the flash welding, a higher secondary wearing voltage must be used, and a large amount of molten metal splashes during the flash welding process. The welder must wear dark protective glasses.
When welding low carbon steel, it is best to use flash welding. The maximum weldable steel section at 20% duty cycle is shown in the technical data sheet.
When welding non-ferrous metals, resistance welding should be used.
The clamping action of the jaws is as follows;
1 first adjust the position of the upper jaw 11 by turning the clamping screw 9 with the handle 6;
2 insert the weldment into the left and right jaws
3 Turn the clamping screw weldment, the welder must ensure that the weldment has sufficient clamping force to weld, otherwise it may cause the machine to burn.
The weldment removal action is as follows;
1 After the welding process is completed, use the handle to loosen the clamping screw;
2, when the hook 7 is removed, the clamping arm is lifted up by the action of the spring;
3 Take out the weldment, pull back the clamp arm, put on the hook, and carry out the next round of welding.
The welder can also work as a card, but must ensure that the workpiece is clamped before welding.
The welding specifications of flash welded parts can refer to the following data;
1 power density; during the burning process, the power density is usually 6-25 A / mm 2, which is 20% lower than the current density required for resistance welding - 50%.
2 welding time; in the case of flash welding without preheating, the welding time depends on the cross section of the weldment and the selected power. When the current density is small, the welding time is prolonged, usually about 2-20 seconds.
3. Burning speed; the burning rate is determined by the power density and the size of the weldment. When welding small surface weldments, the burning rate can be as small as 4-5 mm/sec. When the welding is worn, the burning rate is less than 2 mm/sec.
4 top forging pressure; the top satin pressure is insufficient, which may cause slag inclusion and shrinkage of the weldment. In the absence of preheated flash welding, the upset pressure should be 5-7 kg/mm2. For preheated flash welding, the upset pressure is 3-4 kg/mm2.
5 top forging speed; to reduce the gasification of the metal at the joint, the upsetting speed should be as high as possible, usually equal to 15-30 mm / sec.




2. UN-25-50-100-150 type butt welding machine first selects the jaw according to the shape of the weldment. If the weldment is a bar, the jaw can be directly configured with the welder; if the weldment is shaped, it should be customized according to the shape of the weldment. Jaw.
3. Adjust the jaws; align the two center lines of the jaws, and place the two test bars in the lower jaw positioning groove to see if the two bars are aligned. If it can be aligned, the welder can be used; if it is not right, the jaws should be adjusted. Loosen the fastening screw first when adjusting.
12 Re-adjust the adjusting screw 14 and appropriately move the lower jaw to obtain the best position, and then tighten the fastening wire 12.
4. Adjust the distance of the jaws according to the requirements of the welding process. When the joystick is at the leftmost end, the gap between the jaw electrodes should be equal to the difference between the extension length of the weldment and the amount of extrusion; when the rightmost end of the joystick is used, the electrode spacing is equivalent to the extension length of the two weldments, plus 2-3 Millimeter (ie the original position before welding), this distance adjustment is obtained by the adjusting screw (1). The splicing ruler helps you adjust the parameters.
5. Test welding; in order to prevent the instantaneous overheating of the weldment before the test welding, the number of adjustment stages should be increased step by step. In the flash welding, a higher secondary wearing voltage must be used, and a large amount of molten metal splashes during the flash welding process. The welder must wear dark protective glasses.
When welding low carbon steel, it is best to use flash welding. The maximum weldable steel section at 20% duty cycle is shown in the technical data sheet.
When welding non-ferrous metals, resistance welding should be used.
The clamping action of the jaws is as follows;
1 first adjust the position of the upper jaw 11 by turning the clamping screw 9 with the handle 6;
2 insert the weldment into the left and right jaws
3 Turn the clamping screw weldment, the welder must ensure that the weldment has sufficient clamping force to weld, otherwise it may cause the machine to burn.
The weldment removal action is as follows;
1 After the welding process is completed, use the handle to loosen the clamping screw;
2, when the hook 7 is removed, the clamping arm is lifted up by the action of the spring;
3 Take out the weldment, pull back the clamp arm, put on the hook, and carry out the next round of welding.
The welder can also work as a card, but must ensure that the workpiece is clamped before welding.
The welding specifications of flash welded parts can refer to the following data;
1 power density; during the burning process, the power density is usually 6-25 A / mm 2, which is 20% lower than the current density required for resistance welding - 50%.
2 welding time; in the case of flash welding without preheating, the welding time depends on the cross section of the weldment and the selected power. When the current density is small, the welding time is prolonged, usually about 2-20 seconds.
3. Burning speed; the burning rate is determined by the power density and the size of the weldment. When welding small surface weldments, the burning rate can be as small as 4-5 mm/sec. When the welding is worn, the burning rate is less than 2 mm/sec.
4 top forging pressure; the top satin pressure is insufficient, which may cause slag inclusion and shrinkage of the weldment. In the absence of preheated flash welding, the upset pressure should be 5-7 kg/mm2. For preheated flash welding, the upset pressure is 3-4 kg/mm2.
5 top forging speed; to reduce the gasification of the metal at the joint, the upsetting speed should be as high as possible, usually equal to 15-30 mm / sec.




| UN4-25,100,150 Type butt welder technical parameters | ||||
| Technical project | unit | model | ||
| 25 | 100 | 150 | ||
| Rated power supply voltage U | V | 380-400v | ||
| Rated output power S | KVA | 25 | 100 | 150 |
| X=500/0 output power S50 | KVA | 16 | 63 | 100 |
| Power supply voltage phase frequency | HZ | 1----60HZ | ||
| Rated voltage degree | degree | 8 | ||
| Secondary voltage degree | degree | 7 | ||
| Secondary no-load voltage U20 | V | 1.76-3.52 | 4.5-7. 6 | 5.4-9.5 |
| High and low carbon steel welding section | MM2 | 300 | 1000 | 1400 |
| Copper welded section | MM2 | |||
| Aluminum welding section | MM2 | |||
| Maximum forging force | KN | 30 | 40 | 65 |
| Forging Type | Lever pressure | |||
| Maximum electrode distance | MM | 80 | 80 | 90 |
| Welding productivity | PCS/H | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Cooling water consumption | L/H | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Welder weight | KG | 150 | 450 | 600 |
Send Message